
Digital Tensiometer – measure soil matric potential from 1 to 15 Bar.
Maintenance Free, no need to fill water, digital Modbus RTU over RS485.
Includes protective transport sleeve that can be used to saturate the ceramic tip.
Compatible with the Stevens Steelhead Data Logger
Measures a soil’s matric potential using a precision ceramic and a special positive pressure technique. The FRT15 offers maintenance free long-term stability buried in soil.
A soil’s matric potential is the amount of pressure it takes to pull water out of soil. The higher the pressures, the drier the soil. Most plants and crops are healthiest at -0.33 Bar and plants and crops cannot pull water out of soil during drier conditions beyond -15 Bar. The matric potential is correlated to soil moisture and is an indication of plant water stress.
Matric potential is a negative pressure or a suction commonly referred to by other names such as “soil suction”, “soil tension”, “hydrolic head”, “matric head” or “pF”.
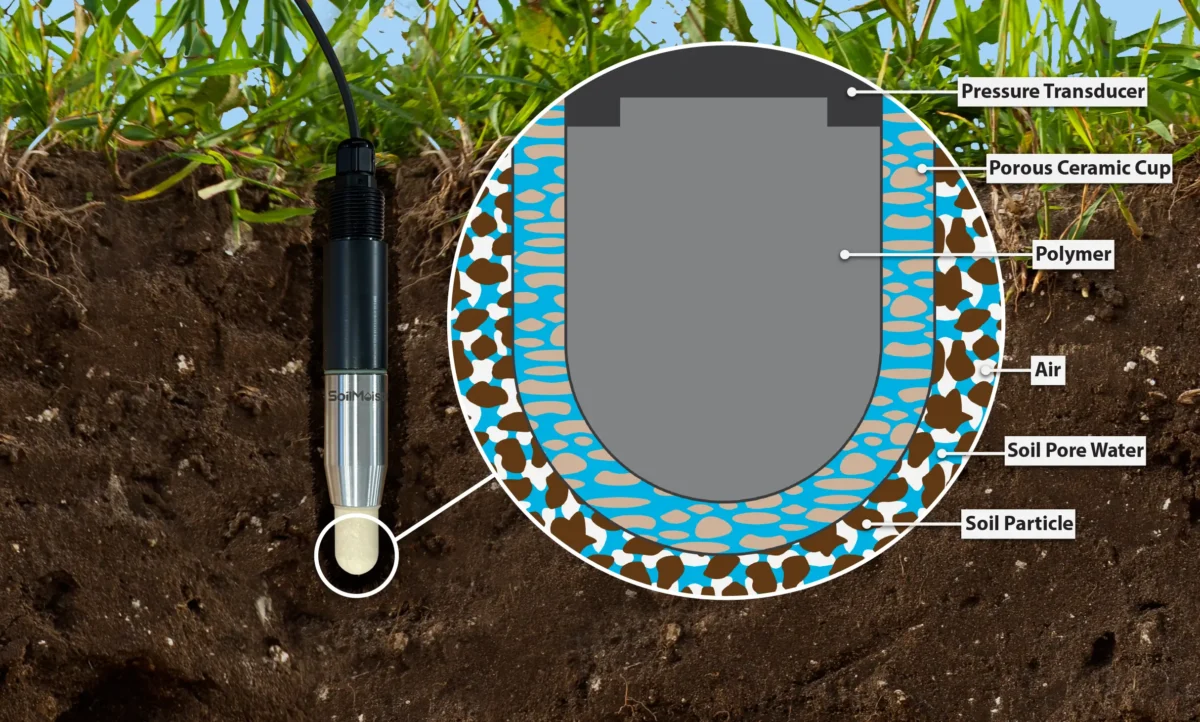
How the FRT15 Works
The FRT15 works differently than a conventional tensiometer. A conventional tensiometer measures the negative pressure suction on water that is at equilibrium with a ceramic in a glass or plastic tube. The ceramic is in contact with the soil which is wicking the water away creating the tension inside the plastic tube. Because a conventional tensiometer measures negative pressure, it will measure matric potential from 0 to -1 Bar.
The FRT15 has a precision ceramic that is in contact with the soil. There is a special polymer between the ceramic and a pressure transducer that is under pressure. The polymer that is under a positive pressure is in contact with the water in the ceramic and is very sensitive to changes in pressure. When the matric potential of the soil changes, it changes the pressure on the polymer. The soil’s matric potential is calculated from the change in positive pressure acting on the polymer.
Request a Quote
Need more information? We’re here to help!
Tell us a bit about yourself and your question and we’ll get back to you ASAP.
Applications
- Irrigation management
- Landslide risk
- Research
- Soil water availability
- Geotechnical applications
Help Unit Conversions Commonly Used for Matric Potential
1 Bar = 10 meters of Hydraulic Head
1 Bar = 100 cBar
1 Bar = 100 kPa
1 Bar = 1000 hPa
1 Bar = 3 pF
Note the pF is the Log base 10 of the pressure in hPa.
Specifications
| Parameter | Dimensions | 2.5cm width X 15cm length |
| Measuring Tip | Ceramic, porus, cylindrical | |
| Cable Length | 5 meters | |
| Pressure Range | -100 to -1500 kPa, or 1 to 15 Bar | |
| Pressure Accuracy | +/- 35 kPa or 2 to 3% FS | |
| Operating Temperature | +1 to 40°C | |
| Electrical | Power Supply | +5 to 30 Volts DC |
| Current Draw, duty cycle and idle | 10 mA max | |
| Communication | Modbus RTU over RS485 | |
| Wire Color | Brown | Power, +5 to 30 Volts DC, optimal |
| White | Ground | |
| Green | A, (-) RS485 | |
| Yellow | B, (+) RS485 | |
| Modbus RTU over RS485 | Baud Rate | 9600 |
| Data Bits | 8 | |
| Parity | Even | |
| Stop Bits | 1 | |
| Flow Control | None | |
| Broadcast Adress | 222 or Hex 0xFD fixed | |
| Slave Address | 1 to 221 (default 1) | |
| Holding Register 2 | Pressure kPa, (internal) | |
| Holding Register 3 | Temperature | |
| Holding Register 4 | Tension, kPa, Matric Potential | |
| Holding Register 5 | Address | |
| Holding Register 6/7 | Serial Number | |
| Holding Register 8 | Firmware |
Downloads
Download Stevens’
Product Catalog




